
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is not commonly used in protein bioprocesses, but for particular products, binding and separation rely on the hydrophobic interaction between resin and protein molecular. The hydrophobic interaction chromatography process features "high salt for binding" and “l(fā)ow salt for elution”, and usually use in series with affinity, ion exchange and gel filtration chromatography steps. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography has high requirements for technologies of hydrophilic surface modification of resin.
Bogen (A Duoning Company) uses high-strength hydrophilic polyacrylate polymer as matrix, and produces hydrophobic resins with uniform distribution, stable structure and strong controllability through industry-leading multi-scale micro-nano structure control technology; meanwhile, we adopt flexible hydrophilic modification technology, to further avoid non-specific absorption, ensuring high recovery rate. Bogen provides customized services of hydrophobic interaction resins with different ligand density, helping users to develop optimum purification process.

Product series
HP series:use for purification of peptide and recombinant proteins
CP series:use for purification of recombinant proteins and antibodies
GP series:use for purification of antigens of vaccines and viruses
Average particle size: 40m、70μm
Ligand types
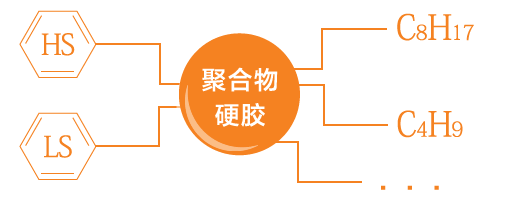
Ligand type is critical factor affecting the selectivity of hydrophobic chromatography resin. Commonly used hydrophobic ligands include: phenyl, octyl, butyl, butylsulfide, butylamine, polyethylene glycol, and polyaldehyde. When the density of hydrophobic ligand is high, for example, more benzene rings or longer hydrophobic chain, both hydrophobicity and protein binding of the resin will be stronger, but difficult to elute when too strong. The order of hydrophobicity of the ligand is: phenyl>octyl>butyl.
Ligand density
The ligand density of hydrophobic interaction chromatography resins should be selected in an appropriate range: , protein molecules are prone to multi-site binding and cannot be eluted if the density is too high, and even causing protein structure changes or denaturation and inactivation; if the density is too low, the protein binding capacity will be low or even cannot bind to resin.
Product features
Series | Product name | Particle size | Pore Size | Max pressure | Max flow rate | Hydrophobic group density |
HP | Phenyl HIC resin(Low density) | 40 μm
70 μm | 30 nm | 10 bar | 1000 cm/hr | 15 μmol/ml |
Phenyl HIC resin(High density) | 35 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(Low density) | 20 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(High density) | 40 μmol/ml | |||||
CP | Phenyl HIC resin(Low density) | 40 μm
70 μm | 100 nm | 10 bar | 1000 cm/hr | 15 μmol/ml |
Phenyl HIC resin(High density) | 35 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(Low density) | 20 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(High density) | 40 μmol/ml | |||||
GP | Phenyl HIC resin(Low density) | 40 μm
70 μm | 500 nm | 10 bar | 1000 cm/hr | 15 μmol/ml |
Phenyl HIC resin(High density) | 35 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(Low density) | 20 μmol/ml | |||||
Butyl HIC resin(High density) | 40 μmol/ml |
Tags
Copyright ? Shanghai Duoning Biotechnology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved Sitemap | Technical Support: 
Message-